Alcohol withdrawal is a common challenge faced by those attempting to reduce or stop their alcohol intake. However, understanding the symptoms and the science behind alcohol withdrawal can make the process less daunting and aid in overcoming this obstacle. This blog post will provide you with valuable insights into alcohol withdrawal symptoms, the underlying science, treatment options, and strategies to prevent withdrawal, ultimately empowering you on your journey to recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize and monitor the range of alcohol withdrawal symptoms for effective management.
- Seek immediate clinical intervention for moderate symptoms to mitigate complications.
- Make healthy lifestyle choices, reduce stress levels, and seek medical help if necessary to prevent alcohol withdrawal and aid in recovery.
Recognizing Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms
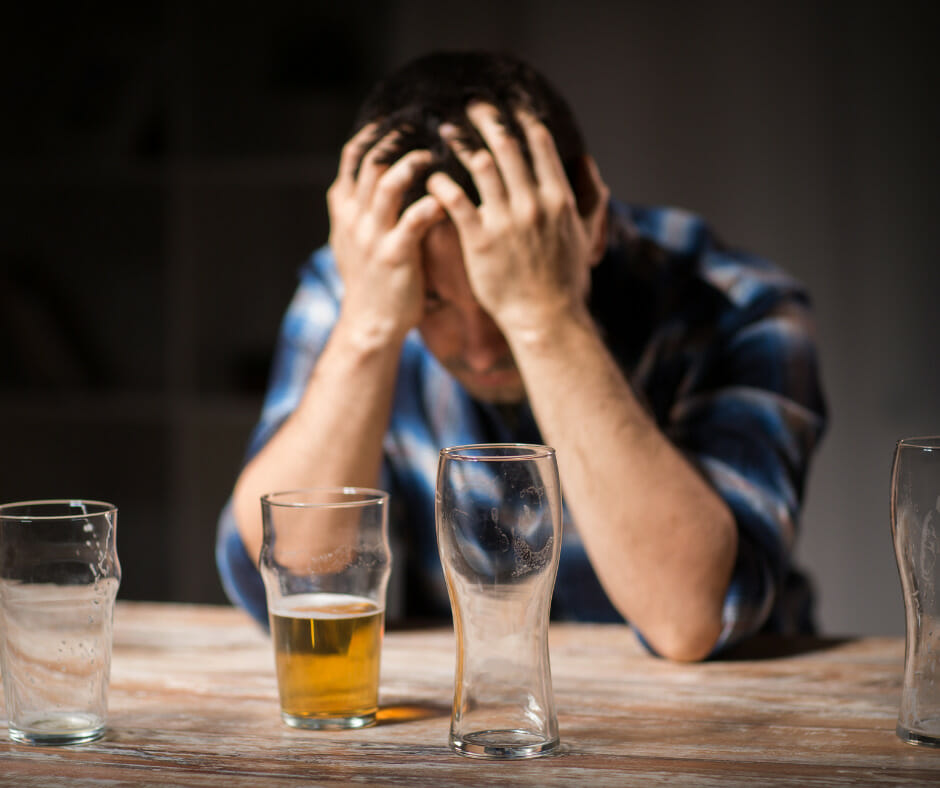

Alcohol withdrawal symptoms can vary greatly in severity, depending on factors such as the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption. Individuals with severe alcohol dependence or a history of substance abuse are more likely to experience more severe withdrawal symptoms, including alcohol withdrawal seizures.
In contrast, those with milder alcohol dependency may only experience mild anxiety or irritability when they stop drinking completely. Comprehending the spectrum of symptoms and their identification is key to managing alcohol withdrawal effectively and safeguarding one’s health.
Mild Symptoms
During the early stages of alcohol withdrawal, individuals may experience mild symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and insomnia. These symptoms are relatively common in alcohol withdrawal syndrome and can often be managed through reassurance and monitoring by treatment staff in a tranquil environment.
Nevertheless, maintaining vigilance as the withdrawal process progresses is crucial, as symptoms may intensify, contingent on the severity of the alcohol addiction and the quantity of alcohol consumed.
Moderate Symptoms
As withdrawal progresses, moderate symptoms may surface, including increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and mild tremors. Individuals experiencing these symptoms should be particularly cautious, as they can be indicative of alcohol abuse and could potentially lead to more serious symptoms such as withdrawal seizures.
These symptoms may also heighten the risk of severe alcohol dependence and complications such as withdrawal seizures, underscoring the need for timely clinical intervention.
Severe Symptoms
Alcohol withdrawal can be severe with serious physical and mental implications. Hallucinations, seizures and delirium are some of the most common and extreme symptoms. These symptoms are considered medical emergencies and require immediate attention.
Individuals experiencing repeated vomiting, severe shaking, or hallucinations due to chronic alcohol consumption should seek immediate medical help. Hospitalization and alcohol withdrawal treatment at an acute care facility or a detox-equipped center are necessary for effective treatment of alcohol withdrawal, particularly for moderate to severe symptoms.
The Science Behind Alcohol Withdrawal

The symptoms of alcohol withdrawal include:
- Tremors
- Sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
These symptoms are a direct result of the brain’s reaction to excessive drinking. When alcohol intake is suddenly decreased or stopped, the brain’s equilibrium between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission is disrupted, resulting in a hyper-aroused state. This state can manifest a variety of withdrawal symptoms within hours of the last drink.
To fully grasp the intricate connection between alcohol use and withdrawal symptoms, we need to investigate the impact of alcohol on the central nervous system and the function of neurotransmitters and receptors.
Central Nervous System
When alcohol is consumed regularly and heavily, the central nervous system (CNS) becomes accustomed to its depressant effects. If the alcohol level suddenly drops, the brain may be affected, resulting in withdrawal symptoms.
According to a research by Richard Saitz of Boston University School of Medicine, alcohol inhibits the ‘fight or flight’ response in the brain and nervous system, which is a natural physiological response to perceived danger. The physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms experienced during alcohol withdrawal are the body’s reaction to this ‘fight or flight’ response.
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
Prolonged alcohol consumption leads to adaptive changes in the brain, which can cause withdrawal symptoms when alcohol is discontinued. Alcohol affects the balance between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate.
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, and alcohol acts as an indirect GABA agonist, increasing its inhibitory effects. When alcohol is removed, an imbalance between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters results, causing withdrawal symptoms.
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline
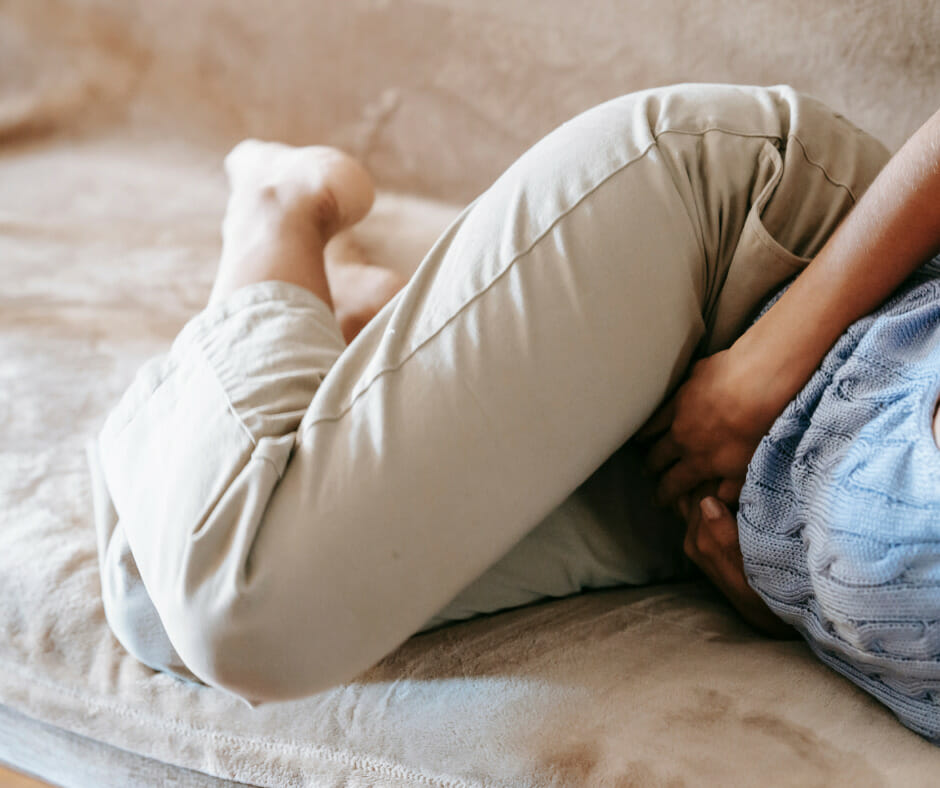

The general timeline for alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be broken down into three stages: initial, peak, and recovery. Symptoms typically begin within hours of the last drink and can last anywhere from three to seven days. However, the duration of withdrawal symptoms may vary depending on the severity and scope of alcohol addiction.
Comprehending this timeline can equip individuals to prepare for and manage their withdrawal symptoms more effectively, thereby enhancing their prospects of a successful recovery.
Initial Stage
During the initial stage of alcohol withdrawal, which typically commences within hours of the last drink, individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- anxiety
- irritability
- nausea
- vomiting
- insomnia
- sweating
- tremors
This stage generally lasts for a few days and can be managed with medical detox, therapy and counseling, and support services to ensure a safe and comfortable withdrawal process.
Peak Stage
The peak stage of alcohol withdrawal is marked by the most severe symptoms, typically occurring around 48 hours after stopping alcohol intake. During this stage, individuals may experience:
- Severe anxiety
- Tremors
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
- Delirium tremens (DTs)
Seeking medical attention during this stage is vital to guarantee proper care and management of symptoms.
Recovery Stage
The recovery stage of alcohol withdrawal follows the peak stage and is characterized by a gradual return to a pre-withdrawal state. Symptoms during this stage may include:
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Tremors
The recovery stage can span from a few days up to several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the alcohol use disorder and the individual’s overall health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Alcohol Withdrawal
Various treatment options are available to help individuals manage and overcome alcohol withdrawal symptoms. These options include medical detox, therapy and counseling, and support services.
Each person’s journey through alcohol withdrawal is unique, requiring the correct blend of treatments and support to safeguard a safe and successful recovery.
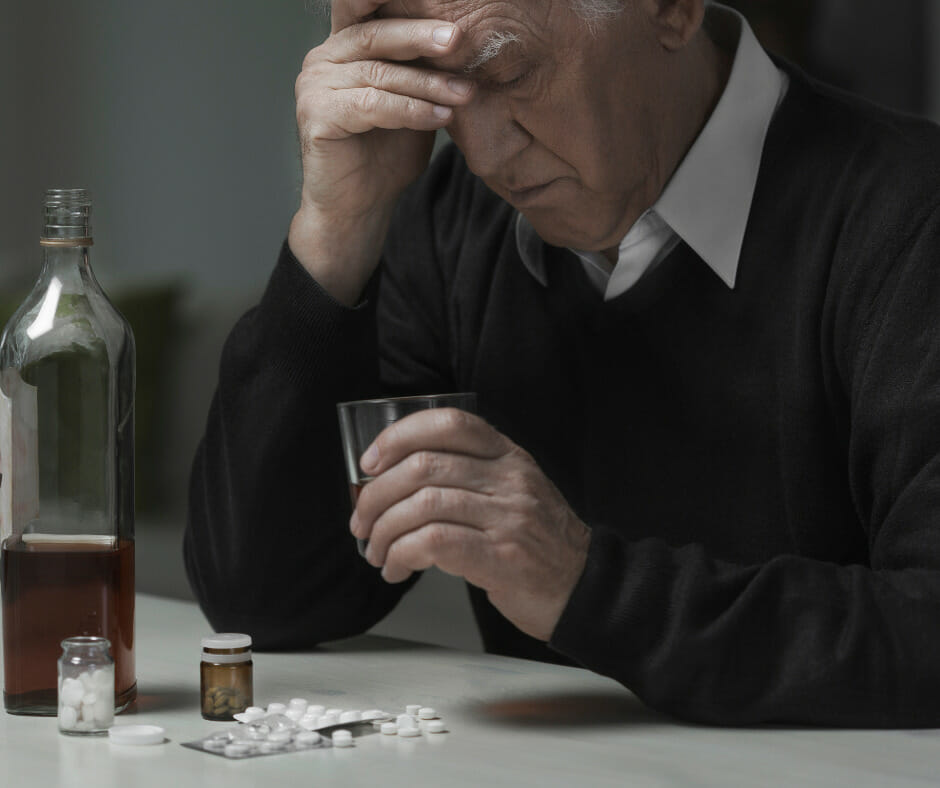
Medical Detox

Medically supervised detox is a critical component of managing severe withdrawal symptoms. It involves inpatient monitoring and the use of sedative medications, such as benzodiazepines, to stabilize the patient and reduce the risk of seizures and other severe withdrawal symptoms. The clinical institute withdrawal assessment is a tool that can be used in this process to evaluate the severity of withdrawal symptoms.
Medical detox ensures the patient’s safety and comfort during the withdrawal process and is often followed by a residential inpatient setting for continued alcohol rehabilitation, therapy, support groups, and other treatments.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling play a vital role in addressing the underlying causes of addiction and preventing relapse. Various forms of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychotherapy, and family therapy, can help individuals understand their addiction, develop coping mechanisms, and find better ways to manage stress and emotions.
Therapy and counseling can also aid in identifying triggers and developing strategies to prevent relapse, ensuring long-term recovery and success. Many recent studies recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for coping with the triggers of relapse during alcohol withdrawal.
According to a study by Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, “the main tools of relapse prevention are cognitive therapy and mind-body relaxation, which are used to develop healthy coping skills.” (Relapse Prevention and the Five Rules of Recovery, Melemis, 2015)
Support Services
Support services like Alcoholics Anonymous and We Are With You provide additional assistance during the recovery process. These services offer a safe and supportive environment for those recovering from alcohol addiction and provide access to resources and support systems to help individuals stay committed to their recovery.
Both online and in-person services are available, ensuring that individuals can find the support they need regardless of their location or personal circumstances.
Identifying Alcohol Use Disorder

Identifying the signs of alcohol use disorder (AUD) is vital for obtaining timely help and treatment. Symptoms such as cravings for alcohol, increased tolerance to the effects of alcohol, and withdrawal when attempting to abstain from drinking are indicative of an AUD.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be struggling with AUD, seeking professional help and making use of resources, such as self-assessment tools and medical consultations, is of utmost importance.
Self-Assessment Tools
Several self-assessment tools are available online to help identify potential alcohol use disorders, including:
- Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)
- CAGE Questionnaire
- Michigan Alcohol Screening Test (MAST)
- Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test – Consumption (AUDIT-C)
These tools can provide a helpful insight into the risk of alcohol use disorder; however, consulting a medical professional for a precise diagnosis and suitable treatment is indispensable.
Seeking Medical Help
Consulting with a medical professional is vital for obtaining a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for alcohol use disorder. If you believe that you or a loved one may be grappling with alcohol addiction, seeking medical help and discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider is crucial.
They can provide guidance on reducing alcohol consumption, recommend appropriate treatments, and offer support throughout your recovery journey.
Preventing Alcohol Withdrawal

Alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be prevented by reducing alcohol consumption and seeking suitable support. Gradually reducing alcohol consumption, adopting healthy lifestyle choices, and utilizing available resources can help minimize withdrawal symptoms and ensure a successful recovery.
It’s important to remember that regardless of the severity of addiction, hope for recovery and a brighter future always exist.
Gradual Reduction
Gradually reducing alcohol consumption can help minimize withdrawal symptoms and reduce the risks associated with severe withdrawal. Tapering off alcohol over time allows individuals to adjust to the physical and psychological changes associated with stopping alcohol consumption.
Regardless of whether the decision is to stop gradually or abruptly, seeking appropriate medical supervision is of utmost importance.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Incorporating healthy lifestyle choices into your daily routine can support your recovery from alcohol addiction and prevent withdrawal symptoms. These choices include adopting stress reduction or relaxation techniques, initiating a regular exercise program, and following a balanced and healthy diet.
Participating in healthy activities and maintaining a strong support network can also help individuals stay committed to their recovery and prevent relapse.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding alcohol withdrawal symptoms, their underlying causes, and available treatment options can empower individuals on their journey to recovery. By recognizing the signs of alcohol use disorder, seeking appropriate medical help, and utilizing available resources, individuals can overcome the challenges of alcohol withdrawal and embrace a healthier, happier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 4 of the withdrawal symptoms?
Common withdrawal symptoms include sweating and/or chills, headaches, digestive issues, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety and insomnia.
How quickly does your body recover when you stop drinking?
Within 72 hours of your last drink, your body will start feeling better and more clearheaded.
As you rest, your systems will return to normal function.
How long does alcohol withdrawal typically last?
Alcohol withdrawal typically lasts three to seven days, depending on the severity of alcohol addiction.
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild to severe, and can include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and tremors. Severe cases may require medical intervention.
What is the most severe manifestation of alcohol withdrawal?
The most severe manifestation of alcohol withdrawal is delirium, which can include hallucinations, seizures, and severe confusion.
These symptoms can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Without treatment, depression can lead to death. Treatment for delirium typically includes medications to reduce the severity of symptoms.
What treatments are available for alcohol withdrawal?
Treatments for alcohol withdrawal include medical detox, therapy and counseling, and support services, such as Alcoholics Anonymous and We Are With You, to help individuals successfully manage the condition.
The post Understanding Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms in 2023 appeared first on Lantana Recovery: Addiction Treatment Rehab Center.
source https://lantanarecovery.com/alcohol-withdrawal-symptoms/

No comments:
Post a Comment